Mandatory Voting or the Right to Choose: Which Path Does Democracy Follow?
WANA (July 05) – Voting is considered one of the most fundamental pillars of democracies. In many countries, voting is recognized as a right, and citizens can decide whether to participate in elections. This approach is based on individual freedom and human rights principles, allowing citizens to engage in the electoral process according to their will and interests.
However, in some countries, voting goes beyond a right and is considered a mandatory duty. By implementing compulsory voting laws, these countries require all eligible citizens to participate in elections.
The primary goal of these laws is to increase public participation in the electoral process and ensure better and more comprehensive representation of all societal sectors. In these countries, failure to participate in elections can lead to fines, deprivation of civil rights, or even restrictions on access to government services.
In this article, we will examine the countries where voting is compulsory. We will discuss the reasons for and against mandatory voting and explore why this law is not fully enforced in some countries. Finally, we will analyze the outcomes and implications of compulsory voting compared to voting as a right.
Through this analysis, we can better understand how these systems can impact democracy and society.
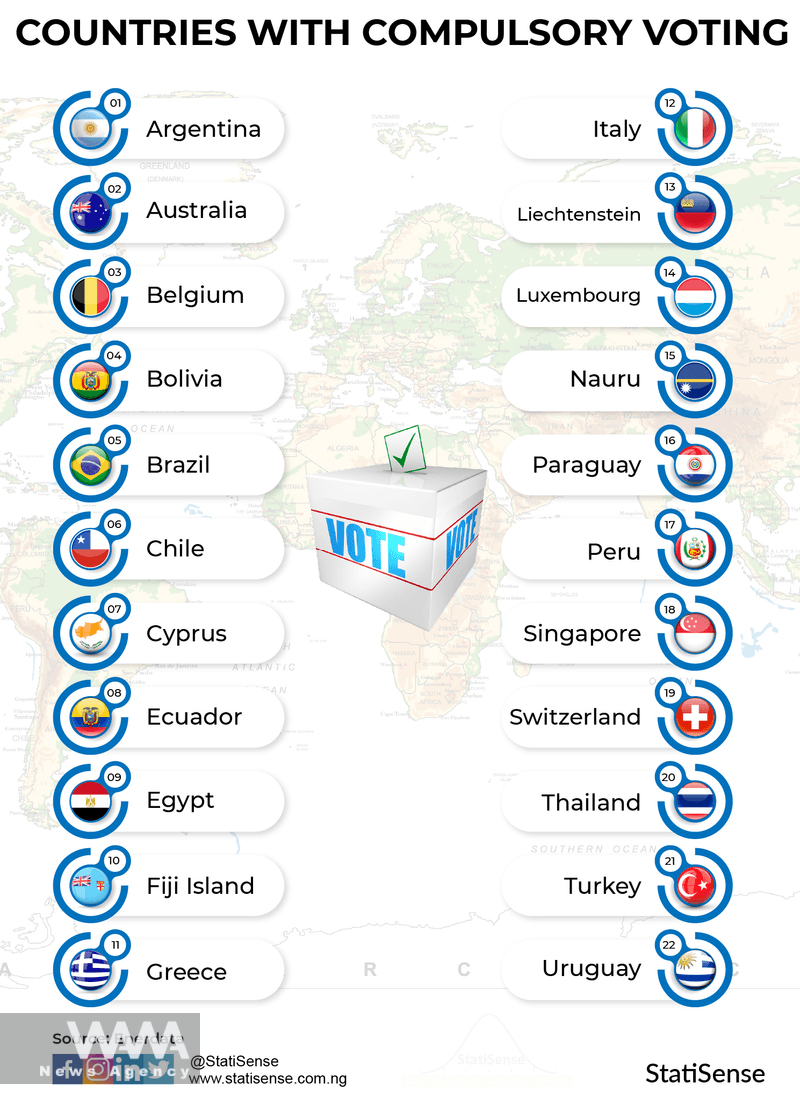
WANA- Countries with Compulsory Voting
Countries with Compulsory Voting
Argentina
Argentina is one of the countries where voting is compulsory. Failure to participate in elections without a valid reason can lead to fines or even restrictions on access to government services. This law in Argentina aims to increase public participation and ensure better representation of all societal sectors.
Belgium
Belgium also has compulsory voting laws. In this country, not participating in elections can result in fines or deprivation of civil rights, including voting rights, in future elections. Belgium is one of the oldest countries to implement compulsory voting, and this law has positively affected public participation over time.
Australia
Australia is another country where voting is compulsory. Failure to attend elections without a valid reason can lead to fines. This country has significantly increased public participation through this law, making election results more representative of a broader spectrum of society.
Reasons for Supporting Compulsory Voting
Increased Public Participation
One of the main reasons supporters advocate for compulsory voting is the increase in public participation in elections. The turnout rate is significantly higher in countries with compulsory voting than in countries with optional voting, ensuring that election results better reflect the opinions and desires of all societal sectors.
Better Representation
Supporters of compulsory voting believe that this type of voting leads to better representation of all societal sectors. In other words, election results will be closer to social realities. This can lead to improved policy-making and government decision-making.
Strengthening Democracy
Compulsory voting can strengthen democracy. This type of voting can ensure that all citizens are involved in the country’s decision-making process, thereby solidifying the foundations of democracy. Additionally, high citizen participation can increase public trust in the electoral and governmental systems.

Reasons Against Compulsory Voting
Violation of Individual Freedom
One of the main reasons opponents argue against compulsory voting is that it violates individual freedom. They believe forcing citizens to participate in elections is against freedom and human rights. They believe every individual should have the right to choose whether to participate in elections.
Increase in Uninformed Votes
Opponents of compulsory voting believe that forcing people to vote can increase uninformed votes. In other words, individuals who are not sufficiently informed about politics for various reasons will be compelled to participate in elections, which can negatively impact the quality of the results. This issue may result in elections where the outcomes do not necessarily reflect the informed and valid opinions of society.
High Implementation Costs
Implementing compulsory voting involves high administrative costs. These costs include tracking absent individuals and imposing fines, which can significantly burden governments. In some countries, these expenses might be so high that effective enforcement of this law becomes challenging.
Non-Implementation of Compulsory Voting Laws
In some countries, these laws are not fully enforced despite compulsory voting laws. There can be various reasons for this, including:
Administrative Limitations
Full implementation of compulsory voting requires appropriate infrastructure and resources, which may not be available in all countries. Without these infrastructures, tracking and penalizing absentees becomes difficult.

Political Considerations
Some governments may refrain from strict enforcement of compulsory voting laws for political reasons, as this could lead to public dissatisfaction. This discontent could negatively impact the government’s popularity and the country’s political stability.
Both compulsory voting and voting as a right have advantages and disadvantages. Compulsory voting can increase public participation and strengthen democracy, but it can also infringe on individual freedoms and increase uninformed votes.
On the other hand, voting as a right respects individual freedom but may result in lower public participation. Therefore, each country must make an appropriate decision in this regard, considering its specific circumstances.
In the end, neither system alone can be deemed the best method in all cases, and each country should choose an appropriate approach by considering its cultural, political, and social conditions.
By WANA writer: R. Hejazi












